Biodiversity Conservation
Relevant SDGs
The Group has positioned "coexistence with Nature" as one of our materiality issues, and is engaged in biodiversity conservation activities, working in cooperation with various stakeholders.
Policy and Basic Approach
In December 2022, at its 15th session, the Conference of the Parties (COP15) to the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) adopted a new biodiversity goal, the Kunming-Montreal Biodiversity Framework. In order to achieve the plan’s vision of a world in harmony with Nature by 2050, all companies must make further efforts. The Seiko Group recognizes that its business activities depend on and simultaneously affect ecosystem services, and believes that the conservation of biodiversity is an important issue in environmental management. Our Group will promote steps toward achieving a Nature-positive※1 outcome through our various businesses. Some of the Group's operating companies are located adjacent to national or prefectural parks, and these businesses are promoting biodiversity conservation activities in accordance with their respective locations and environments.
As a Group, we regularly evaluate our dependence upon and impact on natural capital, and assorted risks and opportunities throughout the value chain. When we operate in locations that are critical to biodiversity, we will take proactive steps to reduce and avoid negative impacts, in accordance with the principle of mitigation hierarchy.※1 We also believe that it is important to educate both executives and employees, as well as to collaborate with various stakeholders, including local communities, in order to conserve biodiversity, and we will promote integrated initiatives, including those focused on climate change and resource recycling.
In addition to disclosing information in accordance with the framework of the Task Force on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TNFD), we will participate in and collaborate with a wide range of initiatives led by other parties.
*1 Nature positive: Stopping and reversing biodiversity loss in order to help Nature to recover what it has lost.
*2 Mitigation hierarchy: Prioritizing measures that produce greater impacts on biodiversity
Response to TNFD Recommendations
TNFD is an international initiative that aims to establish a framework for appropriately assessing and disclosing business risks and opportunities related to natural capital. The taskforce’s final recommendations were published in September 2023.
The Company supports the aims and philosophy of TNFD, and was pleased to register as a TNFD Adopter in October 2025.
We began by conducting an initial survey and disclosure in accordance with the final TNFD recommendations. However, in the future, we plan to conduct surveys related to the importance of ecosystems at our main sites, and promote measures to address whatever risks and opportunities we identify. In addition, we will evaluate the progress of these measures and expand the range of information we disclose.

Governance
The Group Sustainability Committee was established to formulate the Group's policy on sustainability and, based on that policy, to promote action. The Sustainability Committee discusses and resolves important matters related to natural capital that impact biodiversity conservation, and reports directly to the Board of Directors. The Board supervises the Sustainability Committee, and also regularly discusses key matters related to materiality, including coexistence with Nature.
Promotion Structure

Roles
The Board of Directors
At least once a year, the Board of Directors receives a report from the Sustainability Committee summarizing the latter’s resolutions. The Board is responsible for overseeing the Group’s efforts to address issues and for monitoring progress. It also regularly discuss important matters related to natural capital.President (Supervisor of Natural Capital)
Important matters related to natural capital are supervised by the President, who serves as chairman of the Sustainability Committee. He is ultimately responsible for formulating the Group's sustainability-related policies, including important matters related to natural capital, and making all management decisions regarding sustainability-related activities.Sustainability Committee
The Committee is chaired by the President, who is ultimately in charge of managing the Group’s natural capital, and consists of full-time officers, including the officer in charge of sustainability promotion, and presidents of Group companies. Matters related to the Group's materiality, including important issues related to natural capital, are discussed and resolved at two regular meetings each year, and at extraordinary committee meetings whenever necessary, and the details of those resolutions are reported to the Board of Directors. The officer in charge of sustainability promotion plays a key role in developing and executing programs based on the Sustainability Committee’s decisions.
Strategy
We looked at the Group's main business fields objectively, with an eye to the entire value chain, and evaluated their dependence on natural capital and their impact thereon, as well as potential risks and opportunities that this presented.
In the future, we will follow the LEAP approach and deepen our efforts by identifying and assessing "priority areas."
Identification and Assessment of Dependencies and Impacts
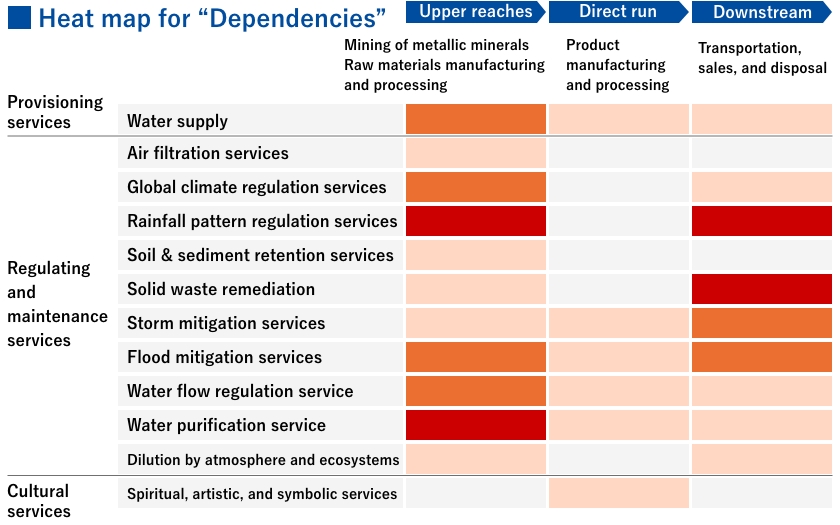
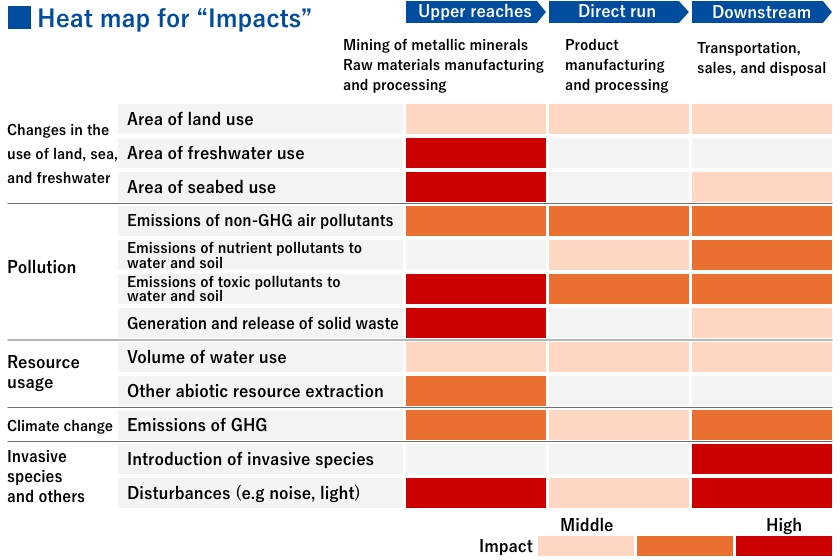
Using ENCORE, an analytical tool that helps organizations understand Nature-related risks and impacts, we identified ecosystem services that are closely related to the activities of the key manufacturing businesses we target. We used a five-point scale to assess their dependency and impact on natural capital, and identified three levels that ranked at least medium or higher. The visualized heat map is shown here.
In terms of dependence, we found that the mining of metal minerals and the production and processing of raw materials upstream of the value chain may depend on ecosystem services such as rainfall pattern regulation and water purification, and downstream, transportation and disposal may depend on ecosystem services such as rainfall pattern regulation and solid waste purification. In terms of impacts, we have identified the possibility that the mining of upstream metal minerals may have an impact such as land modification of freshwater and marine areas, and water and soil pollution due to waste.
Identification and Assessment of Risks and Opportunities
Based on the assessment of the Group’s dependence on and impact on natural capital, we have identified specific risks and opportunities that may have a high financial impact on our business activities. We took a bird's-eye overview of the entire value chain of our main businesses, which allowed us to identify transition risks such as compliance with regulations and soaring procurement costs. On the positive side, we determined that there is room to increase the usage efficiency of resources such as raw materials and water. In the future, we will identify business sites that are highly dependent on and also have a high degree of impact on natural capital, and we will promote specific measures to address the risks and opportunities arising from these dependencies and impacts.
| Risk Classification | Details of Risks | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Risk | Transition | Policies & Regulations | ・Increased cost of procured products due to restrictions on water consumption, tighter regulations on pollution and GHG emissions, tightening of the RoHS Directive, etc., and product development costs due to switching over to alternative products |
| Market | ・Decline in earnings due to inability to respond quickly to consumers’ shift toward more environmentally friendly products | ||
| ・Increased procurement and product development costs stemming from the changing customer preferences noted above | |||
| Technology | ・Increased procurement costs due to increasing costs for the development and deployment of new technology amid the ongoing transition to low-impact technologies | ||
| ・Decline in earnings due to delays in R&D activities to respond to the demand for low-impact technologies | |||
| Opportunity Classification | Opportunity Details | |
|---|---|---|
| Opportunities | Resource Efficiency | ・Cost reductions through the use of recycled raw materials, implementation of the 3Rs, and introduction of production technologies that help reduce GHG emissions
・Stable production and cost reductions by introducing equipment that promotes water conservation and water recycling |
| Market | ・Gain market recognition and increase revenue from products related to biodiversity conservation, such as forest conservation and marine conservation activities | |
Risk and Impact Management
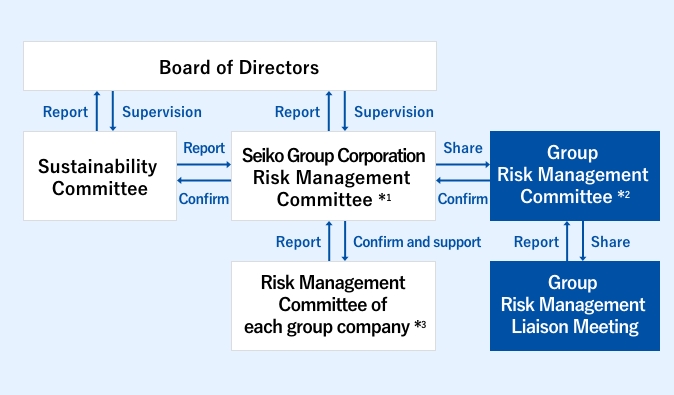
In order to centrally manage risks that could have a significant impact on the Group's business, the Seiko Group Risk Management Committee, chaired by the President of the Seiko Group, plays a central role in developing and strengthening the Group-wide risk management system. In order to promote Group-wide risk management through close cooperation between Seiko Group Corporation (SGC) and its various Group companies, SGC established a Group Risk Management Committee, comprised of the presidents of each Group company, and also established a system to identify and share risks for the entire Group.
We conduct assessments of dependence on and impacts on Nature, as well as risks and opportunities arising therefrom, based on the TNFD's LEAP approach. In particular, the Sustainability Committee identifies and evaluates important dependencies, impacts, risks, and opportunities. It then drafts resolutions, and reports the details of those resolutions to the Board of Directors. In addition, risks addressed by the Sustainability Committee are reported to SGC's Risk Management Committee. In the future, we will consider specific measures to address dependencies and impacts, as well as risks and opportunities, and then make resolutions and promote them within the Sustainability Committee.
Group Risk Management Promotion System
Roles
Seiko Group Risk Management Committee ※1
Chaired by the President, the Committee is working to identify and respond to risks that need to be addressed across the Group. In addition, it receives reports from all the Group risk owners, including at SGC, and supports ongoing risk management at each company.Group Risk Management Committee ※2
Comprised of full-time officers and the presidents of Group companies, this Committee identifies and provides information about risks for the entire Group, monitors responses to key risks, and shares information among all participants.Risk Management Committees of Group Companies ※3
Each Group company promotes risk management autonomously, led by their own risk management committee.Sustainability Committee
The Committee discusses and decides on matters related to the Group's materiality, including Nature-related dependencies and impacts, as well as risks and opportunities, and reports the details of these decisions to the Board of Directors. In addition, it reports to the Seiko Group Risk Management Committee on the progress of measures to alleviate or eliminate risk.
Metrics and Targets
Among several sustainability indicators, the Group quantitatively measures water withdrawal, GHG emissions, waste emissions, recycling rates, and more.
We have set a goal of reducing water withdrawal by 5% in FY2026 (compared to FY2021) and maintaining the level of water withdrawal per unit of sales.
We have also set targets for GHG emissions — reducing Scope 1 and 2 emissions by 42% compared to FY2022, and reducing Scope 3 (Categories 1 and 11) by 25% compared to FY2022, with the aim of achieving net zero emissions by FY2050.
The Seiko Group aims to achieve a recycling rate of over 90% at all domestic sites by fiscal 2030.
While striving to achieve these targets, we will consider adopting additional Metrics and Targets in line with the TNFD disclosure indicators.
Summary of Fiscal Year 2024
In fiscal 2024, as part of our commitment to biodiversity, we worked to reduce water intake through water-saving and recycling initiatives, cut GHG emissions through energy-saving and renewable energy efforts, and promoted waste recycling.
Each Group company also carried out biodiversity conservation activities tailored to their location and surrounding environment, including protection of endangered species, greening initiatives, and awareness programs such as wildlife monitoring and nature observation events.
At Morioka Seiko Instruments, Inc., which has been engaged in conservation activities since 2011, the on-site forest area called “Wakuwaku no Mori / Wakuwaku Tōpu” was officially recognized as a Nationally Certified Sustainably Managed Natural Sites by Japan’s Ministry of the Environment in September 2024.
We will continue to incorporate biodiversity considerations into our product development, making it one of the key criteria for environmentally conscious products.
Examples of Activities
Land use considerations for biodiversity
Protecting Endangered Species
At Seiko NPC Corporation’s Nasushiobara site in Tochigi Prefecture, the company verified the discovery of Kinran and Ginran orchids in the area. Once commonly found in mixed woodlands, these species have been in decline in recent years due to changes in habitat conditions. Tochigi Prefecture has declared both species “Near-Threatened,” and Kinran is also on the Ministry of the Environment’s list of threatened species.
The company monitors these plants and looks forward to their annual blooming. In May 2025, workers identified 34 Kinran and 63 Ginran blooms. Efforts are underway to protect and maintain their habitat. Other orchid species such as Shunran, Yaburan, and Ōbagibōshi have also been observed, highlighting the rich biodiversity of the site.
In 2024, to commemorate the company’s 50th anniversary, it planted moss phlox and flowering peach trees as part of its greening activities.
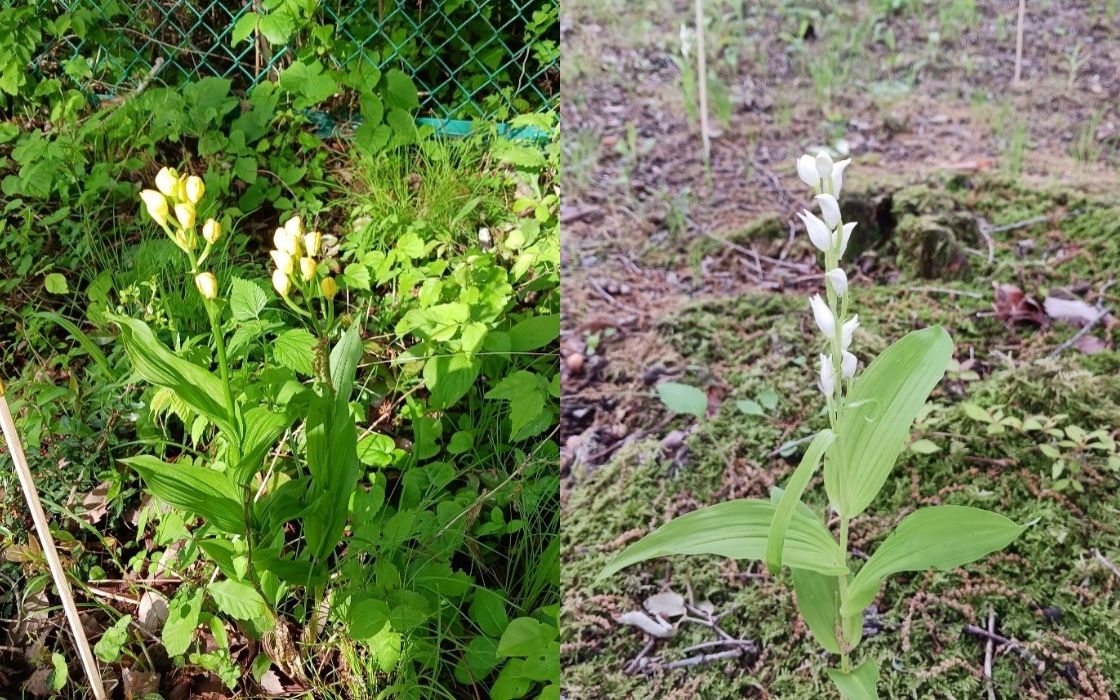

Kinran・Ginran
Conservation of the Endangered Himekomatsu (Japanese White Pine, Pinus parviflora)
Since February 2016, two of Seiko Instruments’s operations in Chiba Prefecture— Takatsuka (Matsudo City) and Ōno (Ichikawa City) — have been cultivating Himekomatsu, a critically endangered pine species designated for protection by Chiba Prefecture. The preservation of the species’ genetic lineage is considered a top priority by local experts.
As part of the prefecture’s Himekomatsu Recovery Plan, both sites are registered as Himekomatsu Genetic Preservation Supporters and actively participate in conservation efforts. The growth of these trees is reported to the prefecture every year in October.
Through such activities, Seiko companies deepen their understanding of biodiversity and strengthen ties with the local community.
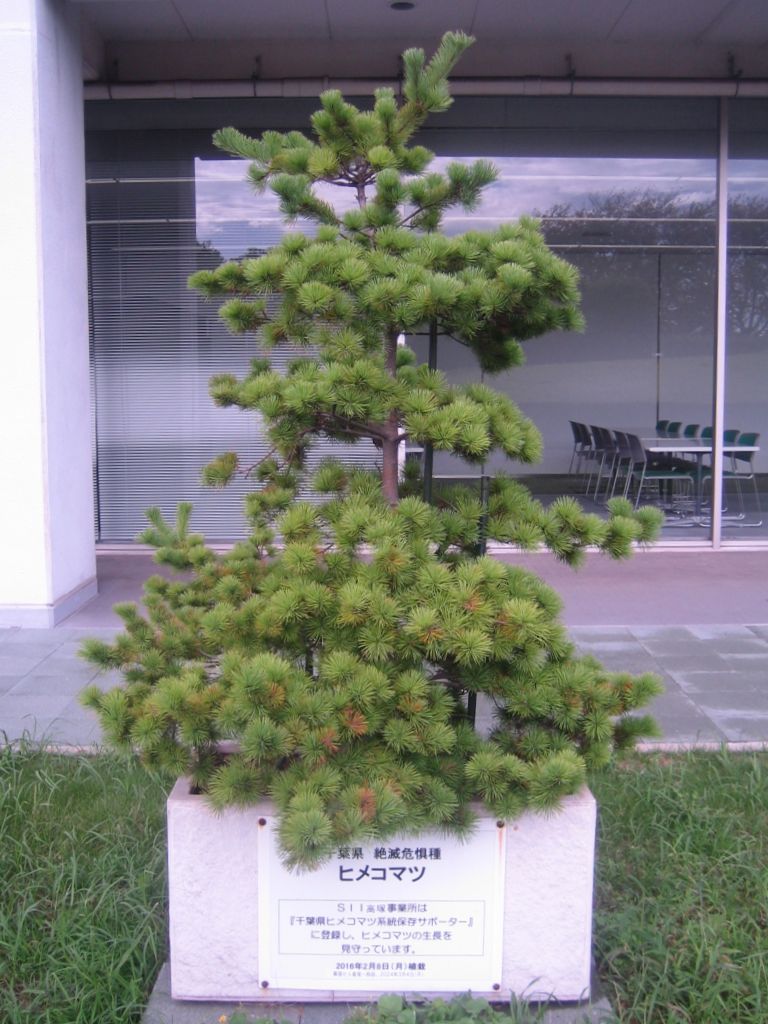

Himekomatsu of Takatsuka site
Greening activities
At SII Crystal Technology Inc., employees continue greening activities on company grounds. In May 2025, 64 employees participated in these efforts, dividing responsibilities by department. They began by clearing vegetation, then planted various seedlings, including moss phlox and annual flowers.
In addition to beautifying the area, these activities also help to foster greater communication among employees.
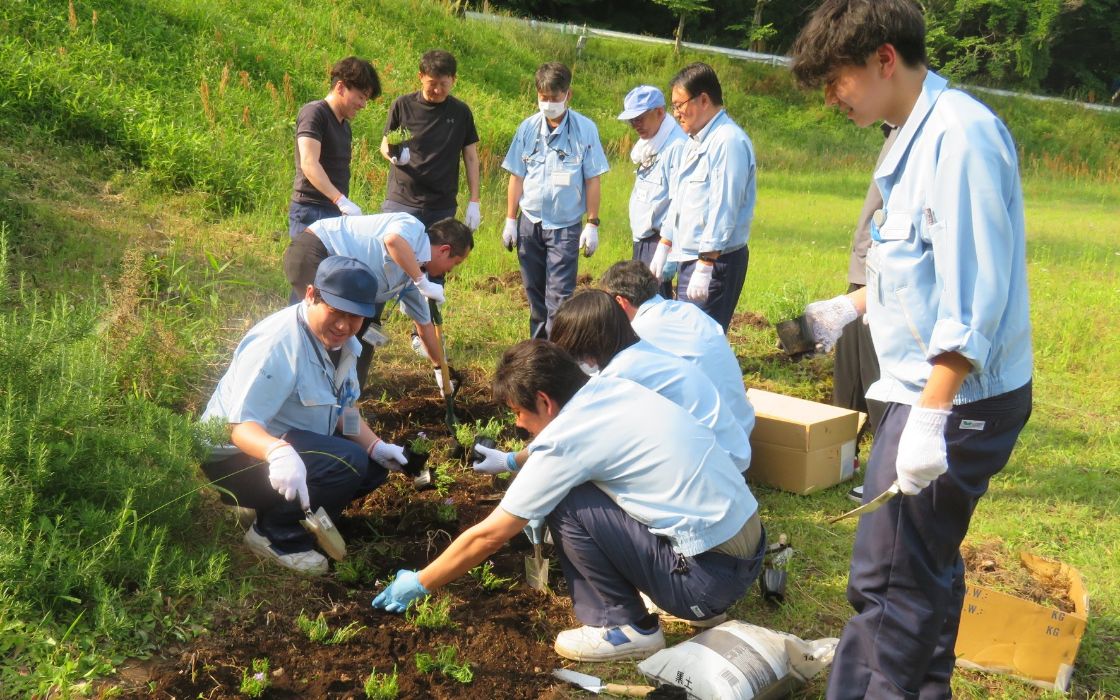

Seedling planting in progress
At Ninohe Seiko Co., Ltd. *, employees actively maintain flower beds as part of ongoing greening efforts. Each department contributes to the creation and upkeep of a total of 52.2 square meters of flower beds.
The company participates in the annual Flower Bed Contest hosted by the Ninohe City Citizens’ Movement Council. In fiscal year 2024, the firm won the runner-up prize, and in 2025, it received the Grand Prize for the first time.
*formerly Ninohe Tokei Kogyo Co., Ltd.
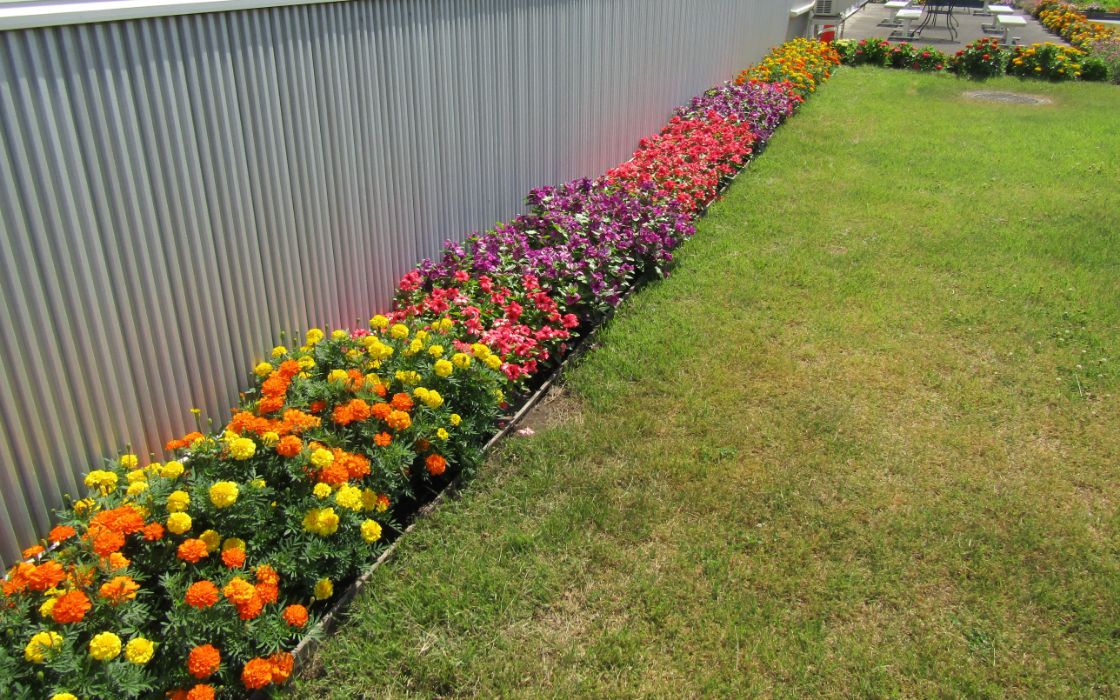

Flower bed created by employees
Dalian Seiko Instruments Inc. in China has been working constantly to create green spaces that support biodiversity. Through its ongoing planting efforts, the firm’s site now features a layered forest structure that ranges from shrubs to tall trees.
To maintain these green spaces, the use of pesticides and herbicides is minimized, and fallen branches and leaves are composted for on-site reuse.
Birdhouses and birdbaths have also been installed, resulting in an increase in both the number and variety of birds visiting the site.
Going forward, the company aims to enhance the quality of existing green spaces and create an environment where diverse flora and fauna can thrive in harmony with the local ecosystem.
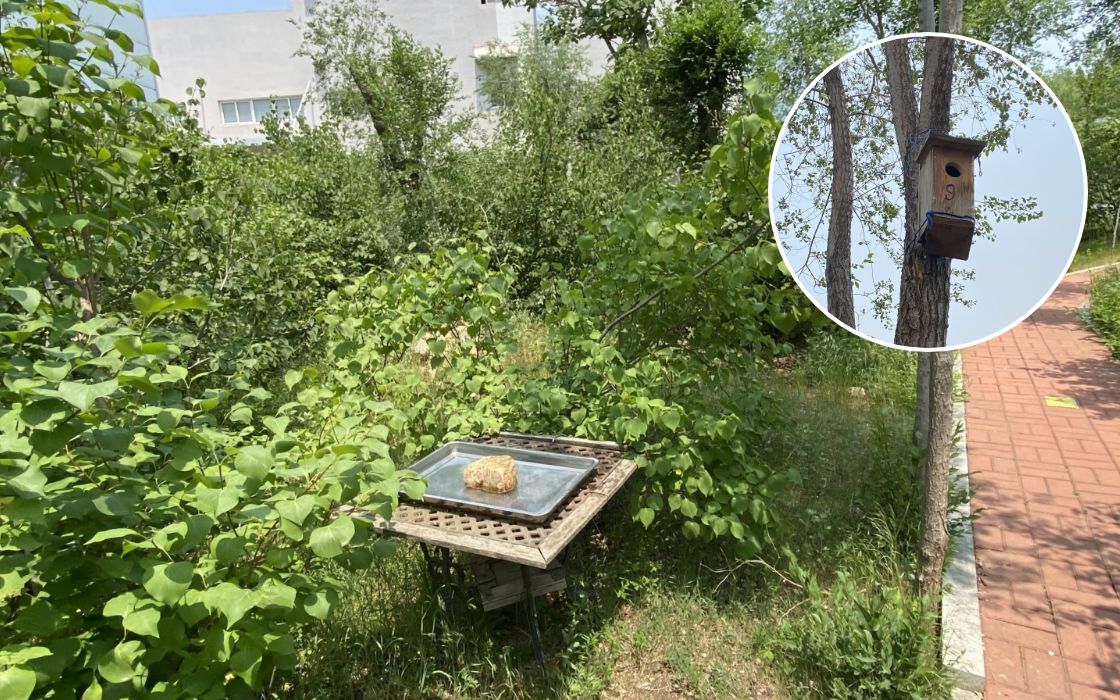

Green spaces of Dalian Seiko Instruments Inc.
Education and awareness-raising activities
Monitoring of living organisms and awareness-raising activities
At various Seiko Instruments Inc. sites, birdhouses and birdbaths have been installed to provide habitats for wildlife. The firm uses sensor cameras to confirm the growing presence of many different species at each site.
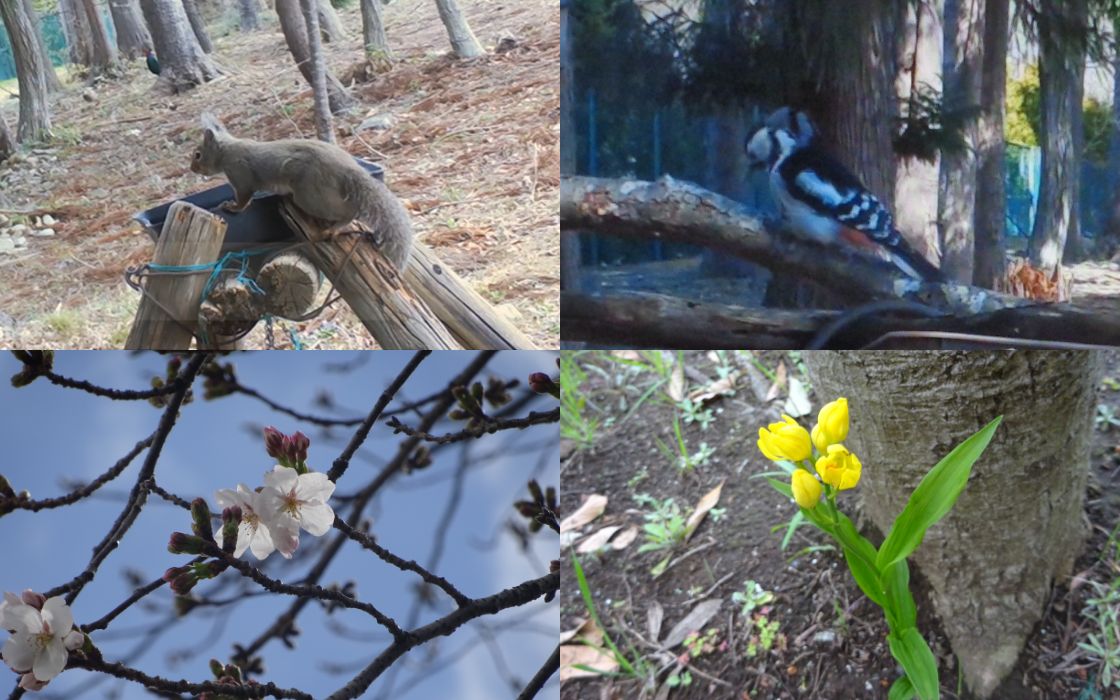

Wildlife Observed at Our Site
The results of these wildlife surveys and recorded videos are used for employee awareness activities, helping to deepen understanding of biodiversity and the range of wildlife living on company grounds.
At the Sendai site, the firm offers a video titled “Introducing Animals That We Coexist With” to help employees’ learn more about the biosphere in which they exist.
At SII Crystal Technology Inc., wildlife survey results are turned into posters to support internal awareness campaigns.

Video Released
Nature Observation Event
Nature Observation Event Held at Morioka Seiko Instruments
In May 2025, Morioka Seiko Instruments Inc. (MSI) and SGC jointly held the 14th Nature Observation Event on MSI’s grounds. This ongoing initiative, which began in 2012, is conducted with the support of Shimizu Corporation and offers participants valuable opportunities to learn about biodiversity conservation from experts in various fields.
This year’s event welcomed 32 participants, including local government officials and environmental representatives from our Group companies. Under the theme “Exploring Connections Among Spring Creatures,” the program focused on the relationship between spring plants and flower-visiting insects, deepening participants’ understanding of ecosystem interconnections. Prior to the event, a preliminary survey was conducted to examine the distribution of plants and insects within quadrats* established in the previous year. On the day of the event, findings from the survey were used to explain the importance of flower-visiting insects and the significance of biodiversity. Many participants said that they had gained a deeper appreciation for the relationships among living organisms and the interconnectedness of ecosystems, reaffirming the importance of biodiversity conservation efforts.
We plan to continue hosting nature observation events with seasonal themes to further promote environmental awareness.
In addition, MSI and SGC regularly host the “Seiko Environment School,” an educational program aimed at teaching children the importance of biodiversity. Activities include building insect hotels** and exploring nature in the forested areas of the site, providing hands-on experiences that foster a connection with the natural world.
*Quadrat: An ecological survey method that involves delineating a square plot of a fixed size to study the organisms within it.
**Insect Hotel: A habitat made from natural materials such as scrap wood, fallen branches, and bamboo, designed to support insect breeding and overwintering, thereby contributing to the creation of diverse ecosystems.
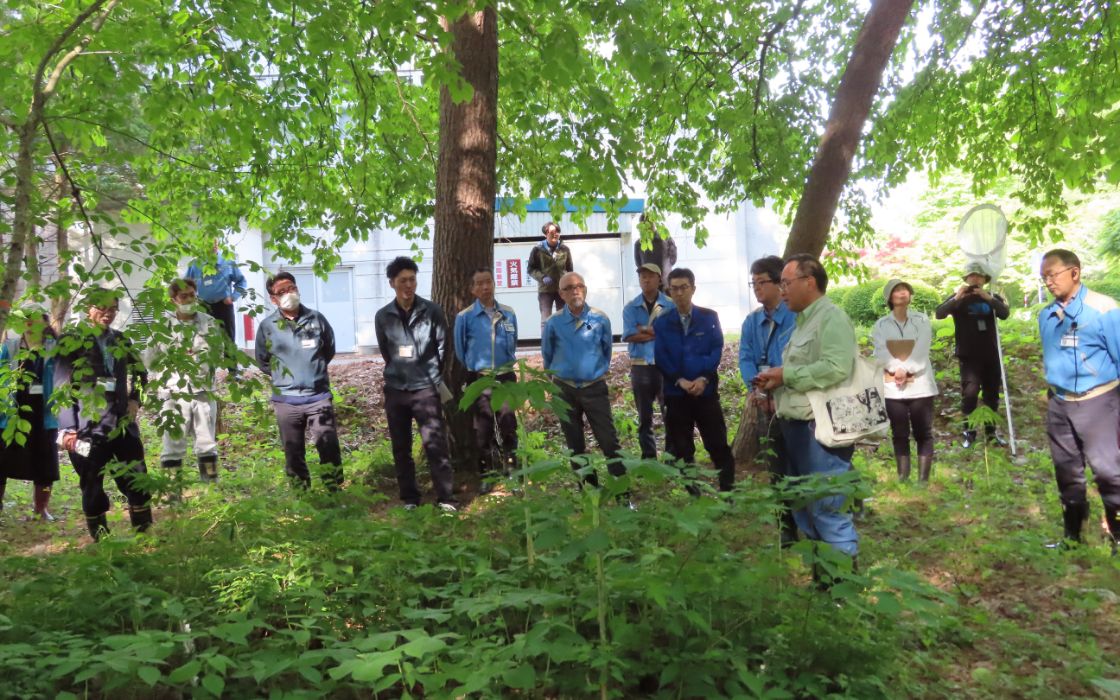

An expert explaining spring plants.
Products and Biodiversity
The Green Product Standards include consideration for biodiversity as one of the environmental criteria. Specific measures, such as minimizing the impact on ecosystems by eliminating lead use, are set for each product. The product standards are reviewed every two years, with a focus on enhancing biodiversity considerations for all products.















